extendedFamily adds new links to R’s generalized linear models. These families are drop in additions to existing families.
Links:
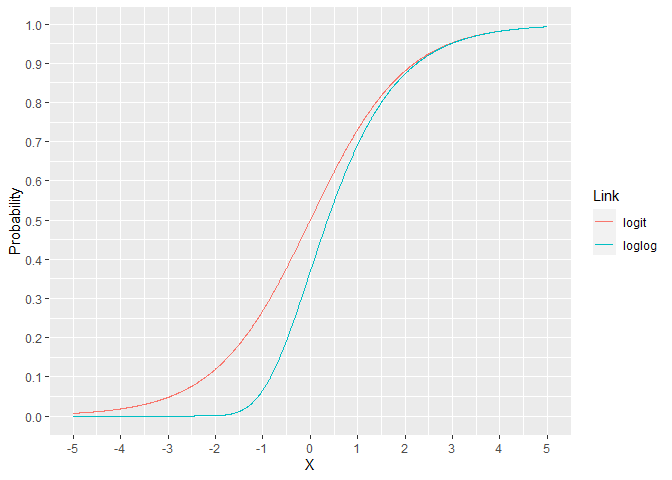
For the binomial family, the link is usually the logit but there are other options. The loglog model assigns a lower probability for X ranging from -5 to 2. For X over 2, the models are essentially indistinguishable. This can lead to improved performance when the response rate is much lower than 50%.
The heart data contains info on 4,483 heart attack victims. The goal is to predict if a patient died in the next 48 hours following a myocardial infarction. The low death rate makes this dataset a good candidate for the loglog link.
data(heart)
heart %>%
summarise(deathRate = mean(death))
#> deathRate
#> 1 0.03925942Only the family object needs to change to use the loglog link.
glmLogit <- glm(
formula = death ~ anterior + hcabg + kk2 + kk3 + kk4 + age2 + age3 + age4,
data = heart, family = binomial(link = "logit")
)
glmLoglog <- glm(
formula = death ~ anterior + hcabg + kk2 + kk3 + kk4 + age2 + age3 + age4,
data = heart, family = binomialEF(link = "loglog")
)AUC improved by changing the link.
predictions <- heart %>%
select(death) %>%
mutate(
death = factor(death, levels = c("0", "1")),
logitProb = predict(object = glmLogit, newdata = heart, type = "response"),
loglogProb = predict(object = glmLoglog, newdata = heart, type = "response")
)
roc_auc(data = predictions, truth = death, event_level = "second", logitProb)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 roc_auc binary 0.797
roc_auc(data = predictions, truth = death, event_level = "second", loglogProb)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 roc_auc binary 0.801The family objects integrate with Tidymodels.
library(tidymodels)
heart <- heart %>%
mutate(death = factor(death, levels = c("0", "1")))
parsnip_fit <-
logistic_reg() %>%
set_engine("glm", family = binomialEF("loglog")) %>%
fit(death ~ anterior + hcabg + kk2 + kk3 + kk4 + age2 + age3 + age4, data = heart)
testPredictions <- parsnip_fit %>%
predict(new_data = heart, type = "prob")
testPredictions <- heart %>%
select(death) %>%
bind_cols(testPredictions)
testPredictions %>%
roc_auc(truth = death, event_level = "second", .pred_1)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 roc_auc binary 0.801